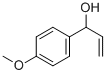
1′-hydroxyestragole(CAS#51410-44-7)
Introduction 1′-hydroxyestragole(CAS#51410-44-7)
Chemical and Physical Properties
Molecular formula: C ₁₀ H ₁₂ O ₂
Molecular weight: 164.20 g/mol
Appearance: Colorless to pale yellow volatile liquid
Boiling point: 277.2 ° C (760 mmHg)
Density: 1.051 g/cm ³ (20 ° C)
Flash point: 119.6 ° C
Vapor pressure: 0.0022 mmHg (25 ° C)
LogP: Approximately 1.723 (moderately lipophilic, easily penetrates biofilms)
Structural features: Phenylpropanoid derivatives, containing methoxy and allyl alcohol side chains, are 1 ‘- hydroxylated metabolites of estragole.
Toxicology and Health Risks
Carcinogenicity:
1 ‘- Hydroxyartemisinin is the main liver carcinogenic metabolite of artemisinin, which induces the formation of liver cell DNA adducts in animal models, significantly higher than the parent compound.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has not yet classified it separately, but the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has banned it as a food additive due to its genetic toxicity.
Mutability:
Chromosome breakage can be induced in HepG2-CYP1A2 cells, indicating a threshold for DNA adduct formation and dose-dependent genotoxicity.
Hepatotoxicity mechanism:
After catalytic hydroxylation by CYP1A2, SULT1A1 is further sulfated to generate highly active electrophilic intermediates that covalently bind to DNA bases (such as guanine), leading to gene mutations and liver cell damage.
Acute toxicity:
GHS classification: GHS07 (health hazard), GHS08 (carcinogenicity)
Hazard description: H317 (may cause skin allergies), H351 (suspected to be carcinogenic), H341 (suspected to be genotoxic), H302 (harmful if swallowed).


![4 6-Dichloro-1H-pyrazolo[4 3-c]pyridine (CAS# 1256794-28-1)](https://www.xinchem.com/uploads/46Dichloro1Hpyrazolo43cpyridine.png)