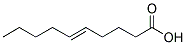
Crotonic acid(CAS#107-93-7)
| Risk Codes | R21/22 – Harmful in contact with skin and if swallowed. R34 – Causes burns R50/53 – Very toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36/37/39 – Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) S61 – Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions / safety data sheets. S37/39 – Wear suitable gloves and eye/face protection |
| UN IDs | UN 2823 8/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | GQ2900000 |
| HS Code | 29161940 |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| Packing Group | III |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 1.0 g/kg (Smyth, Carpenter) |
Introduction
Trans-butenedioic acid (cis-9,10-dihydroxy-9,10-dimethyl-1,2-dihydro-5,6-cyclohexene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid) is an organic compound.Properties:Trans-butenedioic acid is a white crystalline powder that is soluble in water and organic solvents. It has good thermal stability and chemical stability. Trans-butenedioic acid can undergo a dehydration reaction under acidic conditions to form trans-butenedioic anhydride.Uses:Preparation:There are usually two methods for the preparation of trans-butenedioic acid:Oxidize butenedioic acid with vanadium peroxide acid, followed by hydrolysis to obtain trans-butenedioic acid.Perform an acid-catalyzed high-temperature dehydration reaction on butenedioic acid to obtain trans-butenedioic anhydride, followed by reduction and hydrolysis to obtain trans-butenedioic acid.Safety Information:Trans-butenedioic acid is an organic compound with certain toxicity and should avoid direct contact with the skin or inhalation of its dust.During use and storage, fire and explosion protection should be observed, and contact with oxidizers and strong acids should be avoided.Waste that has not been professionally treated should be handled according to local regulations to avoid environmental pollution.