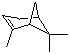
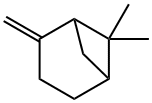
alpha-Pinene(CAS#2437-95-8/80-56-8)
Risk and Safety
| Risk Codes | R10 – Flammable R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. R43 – May cause sensitization by skin contact R50 – Very Toxic to aquatic organisms |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36/37 – Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves. S61 – Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions / safety data sheets. |
| UN IDs | UN 2368 3/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | DT7000000 |
| HS Code | 29021910 |
Introduction alpha-Pinene(CAS#2437-95-8/80-56-8)
Properties
There are two isomers of pinene: α-pinene and β-pinene. α-Pinene is the main component of turpentine, accounting for 86% of the turpentine in maritime pine resin. β-Pinene is a minor component of turpentine, accounting for 5% of the turpentine in maritime pine resin. It is a colorless transparent liquid with the characteristic smell of pine terpene and exists in three forms: levorotatory, dextrorotatory, and racemic. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and acetic acid, and easily soluble in rosin.
Preparation
Obtained by fractional distillation of turpentine under reduced pressure.
Uses
It is an organic synthesis raw material that can be used to synthesize fragrances, camphor, borneol, and other compounds. Pinene can be oxidized by ozone to produce pinic acid, which can be further oxidized to pinic acid derivatives for the preparation of plant growth stimulants, lubricants, plasticizers, etc. Pinene can also be used to make pinene resins and as a solvent for lacquers and waxes.