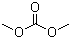Dimethyl carbonate(CAS#616-38-6)
| Hazard Symbols | F – Flammable |
| Risk Codes | 11 – Highly Flammable |
| Safety Description | S9 – Keep container in a well-ventilated place. S16 – Keep away from sources of ignition. S2017/9/16 - |
| UN IDs | UN 1161 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | FG0450000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 2920 90 10 |
| Hazard Class | 3 |
| Packing Group | II |
| Toxicity | LD50 in rats (g/kg): 13.8 orally; 2.5 dermally; LC50 (4 hr) in rats (mg/l): 140 by inhalation (Ono) |
Introduction
dimethyl carbonate is abbreviated as DMC. it is a colorless, transparent and pungent liquid at normal temperature. its relative density (d204) is 1.0694, melting point is 4 ℃, boiling point is 90.3 ℃, flash point is 21.7 ℃ (opening) is 16.7 ℃ (closed), refractive index (nd20) is 1.3687, flammable and non-toxic. It can be mixed with almost all organic solvents such as alcohols, ketones, esters, etc. in any proportion, and is slightly soluble in water. It can be used as a methylation reagent. Compared with other methylation reagents, such as methyl iodide and dimethyl sulfate, dimethyl carbonate is less toxic and can be biodegraded.
In the past, the method of using phosgene as raw material to prepare dimethyl carbonate is not commonly used. Instead, it is prepared by the catalytic oxidative carbonylation reaction of methanol in the presence of oxygen, which is more environmentally friendly than the previous method.
Dimethyl carbonate can methylate aniline, phenol and carboxylic acid, but many reactions require high pressure. DBU can be added when refluxing DMC to catalyze the reaction of dimethyl carbonate methylated carboxylic acid