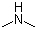
Dimethylamine(CAS#124-40-3)
| Risk Codes | R12 – Extremely Flammable R20 – Harmful by inhalation R37/38 – Irritating to respiratory system and skin. R41 – Risk of serious damage to eyes R34 – Causes burns R20/22 – Harmful by inhalation and if swallowed. R11 – Highly Flammable R39/23/24/25 - R23/24/25 – Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. R52/53 – Harmful to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. R40 – Limited evidence of a carcinogenic effect R19 – May form explosive peroxides |
| Safety Description | S3 – Keep in a cool place. S16 – Keep away from sources of ignition. S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S29 – Do not empty into drains. S36/37/39 – Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) S39 – Wear eye / face protection. S61 – Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions / safety data sheets. |
| UN IDs | UN 2924 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | IP8750000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 3 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29211100 |
| Hazard Class | 3 |
| Packing Group | II |
| Toxicity | Acute oral LD50 for guinea pigs 340 mg/kg, mice 316 mg/kg, rats 698 mg/kg, rabbits 240 mg/kg (quoted, RTECS, 1985). |
Introduction
Dimethylamine is a colorless gas with an ammonia odor. The following is an introduction to the properties, uses, preparation methods and safety information of dimethylamine:Quality:Appearance: colorless gas, soluble in water, can react with inorganic acids and inorganic bases.Odor: Similar to ammonia, it is highly irritating and corrosive.Stability: Relatively stable and not easy to decompose at room temperature.Use:Industrial use: Dimethylamine is mainly used as a solvent and extractant for the synthesis of dyes, resins, softeners and chemical intermediates, among others.Preparation method:Dimethylamine can be prepared by the catalytic reaction of isopropylamine and formaldehyde, and the isopropyl alcohol produced in the reaction is further reacted to form dimethylamine.Another preparation method is through the reaction of ammonia and formaldehyde to produce a condensate containing dimethylamine, which is then hydrolyzed to obtain dimethylamine by dehydration acidification.Safety Information:Dimethylamine is irritating and corrosive, avoiding contact with skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.Avoid inhaling the smell of dimethylamine as it is more irritating.When using dimethylamine, appropriate protective equipment such as gloves, protective glasses and goggles should be worn.A well-ventilated environment should be maintained when storing and handling dimethylamine.