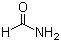
Formamide(CAS#75-12-7)
| Hazard Symbols | T – Toxic |
| Risk Codes | R61 – May cause harm to the unborn child |
| Safety Description | S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) S53 – Avoid exposure – obtain special instructions before use. |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | LQ0525000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 10 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| Toxicity | LD50 in mice, rats (g/kg): 4.6, 5.7 i.p. (Pham-Huu-Chanh) |
Formamide(CAS#75-12-7)
Introduction
Formamide is an amide derived from formic acid, and its molecular formula is HCONH. It is a colorless liquid, miscible with water, and has an odor similar to ammonia. Mainly used in the production of sulfonamides, synthetic vitamins and as a softener for paper and fiber. Pure formamide can dissolve many water-insoluble ionic compounds, so it is also used as a solvent.
physical properties
Colorless odorless oily liquid, slightly ammonia smell when containing impurities. It’s hygroscopic. Relative molecular mass 45.04. Relative density 1.1334. Melting point 2.55 ℃. Boiling point 210.5 ℃. Refractive index 1.4475. Flash point 154 ℃. The viscosity 3.76mpa s(20 ℃). Insoluble in ethers and chlorine-containing solvents, slightly soluble in benzene, and miscible with water, methanol, ethanol, acetic acid, acetone, dioxane, ethylene glycol, phenol and lower esters.
Chemical properties
This product can dissolve casein but not albumin. It can also dissolve casein, glucose, corn protein, gelatin, animal glue, resin, starch, lignin, acetate fiber, nylon and certain inorganic salts: copper, lead, zinc, tin, cobalt, iron, aluminum and nickel Chlorides, certain sulfates, nitrates. The hydrolysis speed of formamide is very slow at room temperature. Increasing the temperature or adding acid and alkali can accelerate the hydrolysis. In the presence of a catalyst, hydrogen cyanide can be separated by heating below 35°C. Formamide has two active functional groups, namely carbonyl and amide groups, which are easy to react chemically and produce many nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds. Formamide can react with inorganic acid to form formic acid and ammonium salt. Reacts with organic halides or alcohols in the presence of a catalyst to form formate. This product can also react with β-diketone, β-iminone, fat couple, aromatic couple, and heterocyclic couple. It can combine with cobalt salt, copper salt and nickel salt to form complexes. When formamide meets a strong dehydrating agent such as phosphorus pentoxide, hydrogen cyanide can be generated. Reacts with phosphorus pentasulfide to produce thioformamide. Formamide can strongly corrode copper, brass, lead and rubber, so attention should be paid when storing and transporting.
Uses formamide is used as softener and solvent for animal glue and paper, for spinning acrylonitrile copolymer, unsaturated amine polymerization, solvent for pharmaceutical production, solvent for purifying grease and the above dissolution items. Used as an intermediate to synthesize imidazole, pyrimidine, 1,3, 5-triazine, caffeine, theophylline, and theobromine. Used as a raw material for dyes, fragrances, pigments, adhesives, textile auxiliaries, paper treatment agents, etc. Raw materials for the production of formic acid and dimethylformamide.
Acute toxicity
LD506.1g/kg in rats and LD503.15g/kg in mice through stomach. Acute symptoms are characterized by damage to the nervous system, respiratory disorders and conjunctivitis, straight convulsions, and death after 3 to 4 days. The threshold concentration for chronic inhalation is 6±4mg/m3. The maximum allowable concentration in the air in the working environment is 30mg/m3 (20ppm) in the United States and 3mg/m3 in the Soviet Union (vapor, absorbed through the skin).
Chemical properties
Clear oily liquid, slightly ammonia smelly. It is hygroscopic. It is miscible with water and ethanol, slightly soluble in benzene, chloroform and ether.
Use
used as raw materials for the synthesis of imidazole, pyrimidine, 1,3, 5-triazine, caffeine, acrylonitrile copolymer spinning, solvent for antistatic coating of plastic products, etc.
Formamide has active reactivity and special dissolving ability. It can be used as an organic synthetic raw material, a paper treatment agent, a softener for the fiber industry, a softener for animal glue, and an analytical reagent for the determination of amino acid content in rice. In organic synthesis, there are many uses in medicine, and there are also many uses in pesticides, dyes, pigments, spices, and additives. It is also an excellent organic solvent, mainly used in spinning and ion exchange resins of acrylonitrile copolymers, as well as anti-static coating or conductive coating of plastic products. In addition, it is also used to separate chlorosilane, purify grease, etc. Formamide can undergo a variety of reactions. In addition to the three hydrogen participating in the reaction, it can also undergo dehydration, deCO, introduction of amino groups, introduction of acyl groups and cyclize. Take the ring as an example. Diethyl malonate and formamide cyclize to obtain the intermediate 4, 6-dihydroxypyrimidine of vitamin B4. Ano-aminobenzoic acid and amide cyclize to obtain quinazolidone -4, an intermediate of anti-arrhythmic roline. 3-amino-4-ethoxycarbonylpyrazole cyclizes with formamide to obtain the xanthine oxidase inhibitor allopurinol. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and formamide cyclize to obtain the anticancer drug ethylimine. Methyl methoxymalonate cyclizes with formamide to obtain the intermediate of sulfonamides -5-methoxy-4, 6-dihydroxypyrimidine disodium.
Used as analytical reagent, solvent and softener, and also used in organic synthesis
used in medicine and pesticide industry
Production method
1. The second step of the one-step method is to form methyl formate from carbon monoxide and methanol under the action of sodium methoxide. In the second step, methyl formate was reammonolysis to generate formamide under the reaction conditions of 80-100 ℃ and 0.2-0.6MPa. This method is less problematic.
2. formic acid method formic acid and methanol first carry out esterification reaction to generate methyl formate, then ammonolysis to generate formamide, and then rectification to separate methanol and impurities to obtain the finished product. This method has tended to be eliminated due to high cost.
3. One-step method directly synthesizes formamide from carbon monoxide and ammonia under the catalysis of sodium methoxide at high pressure (10-30MPa) and 80-100 ℃. 4. Formic acid and urea method. 5. The new method reacts with sodium formate and ammonium salt at a certain temperature and pressure to produce formamide. This method is a domestic patented invention.
Category toxic substances
Toxicity grading poisoning
Acute toxicity oral-rat LD50: 5577 mg/kg; Oral-mouse LD50: 3150 mg/kg
Stimulation data eye-rabbit 100 mg severe
Flammability hazard characteristics are flammable; toxic nitrogen oxide gas is emitted from the fire site
Storage and transportation characteristics warehouse low temperature, ventilation, drying
Fire extinguishing agent carbon dioxide, chemical dry powder