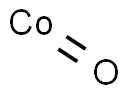Cobalt oxide(CAS#1307-96-6)
| Hazard Symbols | Xn – Harmful
N – Dangerous for the environment |
| Risk Codes | R22 – Harmful if swallowed R43 – May cause sensitization by skin contact R50/53 – Very toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. |
| Safety Description | S24 – Avoid contact with skin. S37 – Wear suitable gloves. S60 – This material and its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste. S61 – Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions / safety data sheets. |
| UN IDs | UN 3288 |
Introduction
Cobalt monoxide (CoO) is an inorganic compound with the form of black crystals. It has the following properties:Higher density: Cobalt monoxide has a density of about 6.44 g/cm³.Magnetism: Cobalt monoxide is an antiferromagnetic material, which exhibits magnetic properties at room temperature.Stability: It is stable in air but susceptible to oxidation in humid environments.Cobalt monoxide has a wide range of applications, including:As a catalyst: It is often used as a catalyst for reactions such as ammonia oxide, selective hydrogenation, and electrochemical hydrogen storage.Electronic materials: Cobalt monoxide has certain semiconductor properties and can be used in electronic components for magnetostrictive materials, energy storage devices, etc.Ceramics: Cobalt monoxide can be used as a ceramic pigment and glass colorant.The main methods for preparing cobalt monoxide are:Thermal decomposition method: Cobalt monoxide is prepared by heating cobalt compounds, such as cobalt salts, cobalt carboxylates, etc. under suitable conditions.Precipitation method: The appropriate cobalt salt is reacted with carbonate or sodium hydroxide to form a precipitate, which is dried and calcined to obtain cobalt monoxide.Cobalt monoxide is irritating to the skin and eyes, and protective gloves and goggles should be worn when operating.Inhalation of cobalt monoxide dust should be avoided to avoid dust generation during operation.Attention should be paid to sealing during handling and storage to prevent it from reacting with wet oxygen in the air and avoid contact with strong acids and strong oxidants.Waste must be disposed of in accordance with local regulations and cannot be dumped at will.