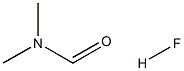
Formamide, N,N-dimethyl-, hydrofluoride (9CI)(CAS#61856-32-4)
2. Physical Properties
Appearance: Typically a colorless to pale yellow transparent liquid with hygroscopic properties.
Boiling Point: No distinct single boiling point; prone to decomposition upon heating, releasing hydrogen fluoride and DMF. Distillation and purification are typically performed under reduced pressure.
Solubility: Soluble in polar organic solvents (such as DMF, methanol, ethanol, dichloromethane, etc.), and upon contact with water, it dissociates, releasing hydrogen fluoride and forming an aqueous solution of DMF.
Density: approximately 1.05–1.10 g/cm³ (at 25°C, with slight variations depending on purity).
3. Chemical Properties
Acidic: As a hydrate of hydrofluoric acid, it exhibits certain acidity and can provide fluoride ions, commonly used as a fluorinating agent in organic synthesis.
Stability: It remains relatively stable when stored sealed and dry at room temperature; it decomposes upon contact with water or strong alkalis, releasing hydrogen fluoride gas; under high-temperature conditions, it readily decomposes, producing irritating and corrosive gases.
Reactivity: It can participate in nucleophilic fluorination reactions, introducing fluorine atoms into organic molecules, and also serve as an acidic solvent in certain catalytic reaction systems.
4. Primary Uses
Organic synthesis reagents: Used as mild fluorinating agents, they are widely applied in the synthesis of intermediates for pharmaceuticals, pesticides, fluorinated materials, and other fields, such as the preparation of fluorinated aromatics and fluorinated heterocyclic compounds.
Acidic solvent: Serves as a solvent in specific organic reactions, simultaneously functioning as both a solvent and a source of acidic conditions, thereby enhancing reaction efficiency and selectivity.
Industrial Applications: Used in small quantities in the electronic chemicals sector as a raw material for the synthesis of fine fluorides.
5. Safety and Storage Instructions
(1) Hazardousness
Corrosive: Strongly corrosive and irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory mucous membranes, causing burns upon contact.
Toxicity: Inhalation of its vapors or mist droplets may cause respiratory irritation, coughing, chest tightness, and other symptoms. Prolonged or repeated exposure may damage the liver and kidneys.
Environmental hazards: Hydrofluoric acid released upon contact with water can contaminate water bodies and soil, posing high toxicity to aquatic organisms.
(2) Storage Requirements
Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated warehouse, away from fire sources and heat sources, with a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
It should be stored separately from alkalis, oxidizers, water, alcohols, etc., and must never be mixed with them.
The storage container must be made of fluorine-resistant materials (such as PTFE or HDPE containers) and equipped with moisture-proof measures.
(3) Operation Precautions
The operator must wear protective equipment, including anti-corrosion gloves, goggles, gas masks, and protective suits.
The operation must be conducted within a fume hood, avoiding direct contact with skin and eyes, and inhalation of vapors is strictly prohibited.
In case of leakage, protective equipment must be worn for handling, and the spill should be absorbed with sand or inert adsorbent materials to prevent contact with water sources.