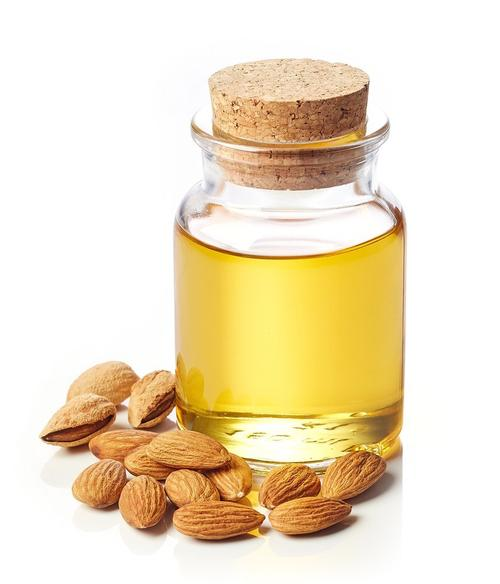
Bitter almond oil(CAS#8013-76-1)
| Hazard Symbols | Xn – Harmful |
| Risk Codes | R20/21/22 – Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36 – Wear suitable protective clothing. |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
Introduction
Bitter almond oil is an oil extracted from bitter almonds. Its main characteristics include:Smell: Bitter almond oil has a strong bitter almond scent.Composition: The main component of bitter almond oil is cyanogenic glycosides from bitter almonds, especially the compound amygdalin.The main uses of bitter almond oil are:Medicinal: The cyanogenic glycosides in bitter almond oil have certain medicinal applications. For example, after hydrolysis, they can produce cyanide, which can be used to treat certain diseases.The general method for producing bitter almond oil includes the following steps:Material preparation: Peel the bitter almonds and grind them into powder.Distillation: Place the powdered bitter almonds in distillation equipment and use an appropriate solvent for extraction by distillation.Purification: Purify the bitter almond oil through the distillation process.Toxicity of cyanogenic glycosides: The cyanogenic glycosides in bitter almond oil are toxic, and excessive intake may lead to cyanide poisoning. Careful dosage control is necessary when using bitter almond oil.Allergic reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to bitter almond oil, so it is important to be aware of individual differences and avoid contact or ingestion as needed.Storage precautions: Bitter almond oil should be stored in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated place, avoiding direct sunlight or high temperatures to maintain its quality and stability.